CESIUM REMOVAL
Marshallton Research Laboratories (MRL) makes calixarene extractants which are highly selective for cesium in the presence of other cations such as sodium and potassium. Fields of use include remediation of radioactive nuclear waste and processing used nuclear fuel (UNF).
MAXCalix e and BEHBCalix f are new cesium extractants with superior solubility properties and greatly improved efficiency. They can process higher-curie feeds and accommodate streams with heavier loadings of potassium. MAXCalix is utilized in the next-generation solvent (NGS) h,i, which has been demonstrated at the pilot plant scale and is now deployed at the DOE SWPF.
Cesium extractant BOBCalixC6 was invented by Oak Ridge National Lab for the removal of radioactive cesium-137 from aqueous feedstocks. Cs-7SB Modifier improves the solubility of BOBCalix in the formulated solvent system, and increases its effectiveness in capturing cesium ions. They are key components for Caustic-Side Solvent Extraction (CSSX) and Fission-Product Extraction (FPEX) c processes. CSSXis now in service at the Salt Waste Disposal Facility (SWPF) at the DOE Savannah River site.
Originally designed for reprocessing used nuclear fuel, MAXCalix is well-adapted for applications involving nitric acid media.
Further reading
(a) B.A. Moyer, et al. (2001) “Calixarene crown ether solvent composition and use thereof for extraction of cesium from alkaline waste solutions”. US Patent 6,174,503.
(b) L.H. Delmau, et al. (2002) “Caustic-Side Solvent Extraction: chemical and physical properties of the optimized solvent” Oak Ridge National Lab Report ORNL/TM-2002/190.
(c) J.Law, et al. (2008) “Simultaneous separation of cesium and strontium from spent nuclear fuel using the Fission-Product Extraction process”. Solvent Extraction: Fundamentals to Industrial Applications: Proceedings of ISEC 2008 International Solvent Extraction Conference, Vol. 1, 659-664.
(d) M.R.Poirier, et al.(2008) “Full-scale testing of a Caustic Side Solvent Extraction system to remove cesium from Savannah River site radioactive waste”. Separation Science and Technology, 43:2797-2813.
(e) E.A. Brass et al. (2008) “First plant-scale operation of Caustic-Side Solvent Extraction process for removal of cesium at the Savannah River site”. Presentation at 18th International Solvent Extraction Conference, Tucson, Arizona, September 15-19, 2008.
(f) D.R. Peterman, et al.(2012) “Extractant compositions for co-extracting cesium and strontium, A method of separating cesium and strontium from an aqueous feed, and calixarene compounds” US Patent 8,158,088.
(g) L.H. Delmau, et al.(2009) “Alternatives to nitric acid striping in the Caustic-Side Solvent Extraction (CSSX) process for cesium removal from alkaline high-level waste”. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 27:172-198.
(h) B.A. Moyer, et al.(2011) “Development of the Next-Generation Caustic-Side Solvent Extraction (NG-CSSX) process for cesium removal from high-level tank waste” WM2011 Conference Paper no. 11346.
(i) T.B.Peters, et al. (2011) “Results of Cesium Mass Transfer Testing for Next Generation Solvent with Hanford Waste Simulant AP-101”. SRNL-STI-2011-00559 Revision 0 .
(j) R. Piecer, et al. (2012) “Performance testing of the Next-Generation CSSX solvent with actual SRS tank waste”. Separation Science and Technology, 47:2088-2097.
(k) D.Campbell (2013) “SRS Salt Waste Processing: 5 Years of Success”. www.srs.gov. SRS News Releases, April 22, 2013.
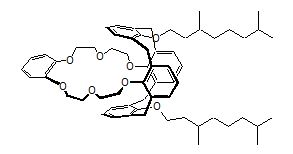
Item# MAXCalix
Compound Description: 1,3-alt-25,27-Bis(3,7-dimethyloctyloxy)calix[4]arene-benzocrown-6
CAS# [1227059-50-8]
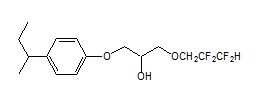
Item# Cs-7SB Modifier
Compound Description: 1-(2,2,3,3,-Tetrafluoropropoxy)-3-(4-sec-butylphenoxy)-2-propanol
CAS# [308362-88-1]
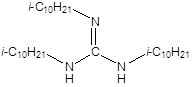
Item# TiDG
Compound Description: N,N’,N’’-Tris(3,7-dimethyloctyl)guanidine
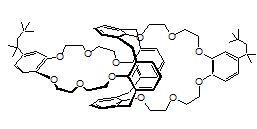
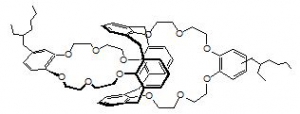
Item # BOBCalixC6
Compound Description: Calix[4]arene-bis(t-octylbenzo-crown-6)
CAS# [220969-34-6]
Item # BEHBCalixC6
Compound Description: Calix[4]arene-bis(2–ethylhexylbenzo-crown-6)
CAS# [757196-34-2]